Manufacturer Of High Quality Data Cable
Manufacturer Of High Quality Data Cable

Every modern gadget, like phones and laptops, uses USB connections, which come in various USB interface types. These connections help transfer data, charge devices, and send video or sound. For instance, USB Type-C is very popular. It moves data super fast, up to 10 Gbps, and delivers power up to 100 watts, perfect for quick charging.
Knowing about USB interface types helps you pick the right cables and devices. The USB Type-C market is expected to grow from $4.66 billion in 2024 to $81.31 billion by 2037. This shows how important these connections are for the future. Whether you're plugging in a keyboard or sharing files, USB makes tech easier to use.
l USB Type-C is very useful. It handles data, charging, and video in one cable.
l Knowing USB types helps you pick the best cables and devices for faster transfers and better charging.
l USB 3.2 is super fast, reaching speeds up to 20 Gbps. It's great for gamers and video editors who need quick file sharing.
l Older USB devices can still work with new ports. This makes upgrading easier without buying all new gadgets.
l USB Power Delivery (PD) charges devices faster by changing voltage. It works well for phones, tablets, and laptops.
USB 1.0 came out in 1996 and started the USB era. It had two speeds: 1.5 Mbps (slow) and 12 Mbps (faster). This version let you plug in devices without restarting your computer. But, it wasn’t widely used because it was still new.
In 1998, USB 1.1 improved on USB 1.0. It kept the same speeds but worked better with slower devices. This made it more useful. Apple helped make USB 1.1 popular by using it in the iMac G3. It became the go-to for connecting things like keyboards and printers.
Fun Fact: USB 1.1 was the first version people used a lot. It set the stage for today’s USB types.
USB 2.0 launched in 2000 and was much faster. It could transfer data at 480 Mbps, 40 times faster than USB 1.1. This made moving big files, like videos, quicker. USB 2.0 also let some devices, like webcams, get power from the USB port.
It became very common in gadgets like flash drives and game controllers. Many devices still use USB 2.0 because it works well and is affordable.
Metric | USB 2.0 | Earlier Versions |
Data Transfer Speed | 480 Mbps | Up to 12 Mbps |
Power Delivery | Limited | Limited |
Data Encoding Efficiency | Standard | Basic |
USB 3.0 came out in 2008 and made data transfer super fast. It could move data at 5 Gbps, great for HD videos or big files. It also improved charging, offering up to 4.5 watts. You could still use older USB devices with it.
In 2013, USB 3.1 got even better. It doubled the speed to 10 Gbps and could deliver 100 watts of power. This made it perfect for charging laptops and powering bigger devices. USB 3.1 also introduced the USB Type-C connector. This connector could handle data, power, and video all in one cable.
USB version | Max. Speed | Charging Power |
USB 3.0 | 5 Gbps | 4.5 W |
USB 3.1 | 10 Gbps | 100 W |
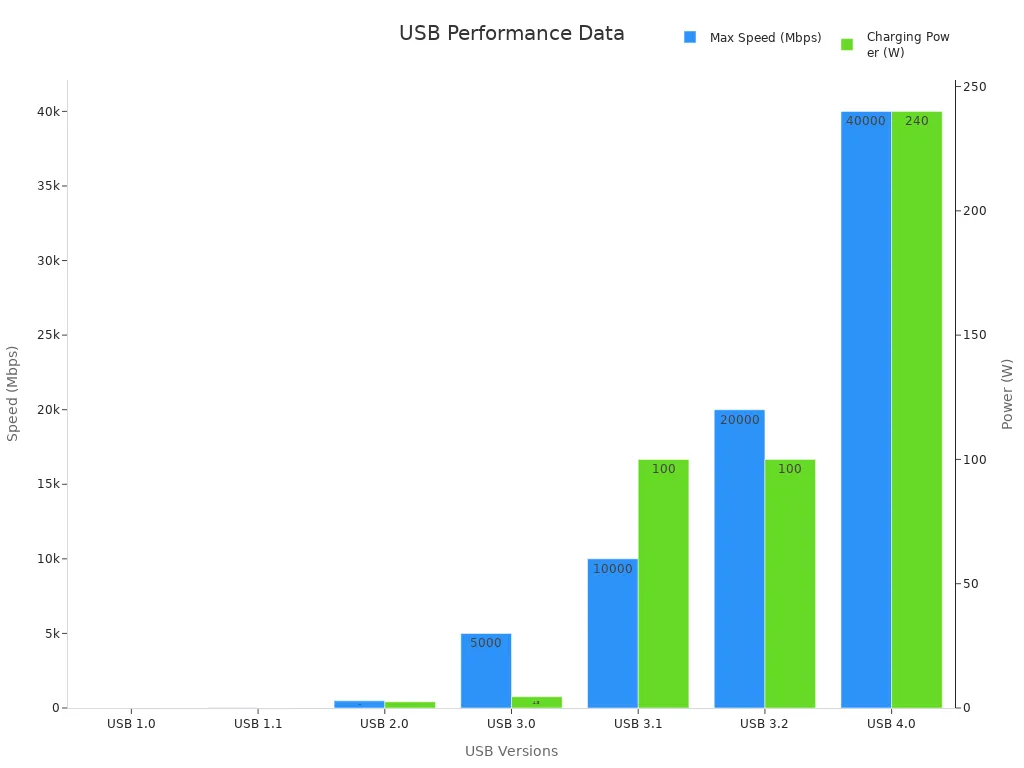
Tip: Want faster speeds and better charging? Try USB 3.1 with Type-C!
USB 3.2 is a big step forward for USB interface types. Released in 2017, it made data transfer faster and more efficient. Think of it as an improved version of USB 3.1 with better speed and performance.
l Enhanced Speed: It can transfer data at speeds up to 20 Gbps. This is double the speed of USB 3.1, great for moving large files like 4K videos or photos.
l Multi-Lane Operation: It uses two lanes to transfer data faster without slowing down.
l Backward Compatibility: Older USB devices still work with USB 3.2 ports but at their original speeds.
Tip: For the fastest speeds, look for "USB 3.2 Gen 2x2" devices. These use two lanes to reach 20 Gbps.
USB 3.2 works best with USB Type-C connectors. These connectors are easy to use because they are reversible. You can also use them for power delivery and video output, making them very useful.
USB 3.2 is great for gamers, video editors, and anyone needing fast data transfer. It works well with external hard drives, monitors, and other devices. If your device supports USB 3.2, you’ll enjoy quicker file transfers and better performance.
USB4 is the newest and most advanced USB interface type. Launched in 2019, it combines the best features of older versions and adds new ones. You’ll find USB4 in high-end laptops, tablets, and other modern gadgets.
1. Blazing Fast Speeds: USB4 can transfer data at speeds up to 40 Gbps. This is four times faster than USB 3.2 and as fast as Thunderbolt
2. Universal Compatibility: It works with Thunderbolt 3 devices, giving you more ways to connect gadgets.
3. Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation: USB4 splits bandwidth between data and video for the best performance.
4. Simplified Naming: Unlike older versions, USB4 has no confusing labels like "Gen 1" or "Gen 2." Just look for "USB4" to know it’s top-notch.
Note: USB4 needs USB Type-C connectors. To use all its features, you’ll need a Type-C cable.
USB4 is perfect for professionals and tech lovers. Use it to connect multiple monitors, move huge files, or power heavy-duty devices. It’s also great for docking stations, letting you connect many gadgets with one cable.
Feature | USB4 | USB 3.2 | USB 3.1 |
Max Speed | 40 Gbps | 20 Gbps | 10 Gbps |
Thunderbolt Support | Yes | No | No |
Bandwidth Allocation | Dynamic | Fixed | Fixed |
USB4 makes connecting devices easier and faster. If you’re upgrading, choosing USB4 will prepare you for future technology.

When you plug in devices, you use different USB connectors. Each type has special features for specific uses. Let’s look at the most common ones: USB-A, USB-B, and USB-C.
USB-A is the most familiar connector. You’ve seen it on flash drives and keyboards. It has a rectangular shape and plugs in one way only. You must align it correctly to connect it.
l Durability: USB-A connectors are strong and last a long time. They meet standards for good signal quality, ensuring smooth data transfer.
l Performance: USB-A adaptors have a slight delay, between 18 ms and 23 ms. Even with this, they work well for daily tasks.
l Compatibility: USB-A works with older versions like USB 2.0 and USB 3.0. This makes it useful for older devices.
Tip: Always align USB-A properly to avoid damaging the port.
USB-B connectors are less common but still important. They are used for printers, scanners, and hard drives. Their square shape makes them easy to recognize. USB-B is bigger than USB-A and USB-C, so it’s not used in small gadgets.
l Specialized Design: USB-B is made for high-power devices like printers. It handles power and data transfer well.
l Reliability: USB-B connectors are sturdy and last through frequent use. They keep connections stable for smooth data transfer.
l Note: USB-B isn’t as flexible as USB-C but is great for durable, high-power needs.
USB-C is the newest and most advanced connector. It came out in 2014 and is small, reversible, and full of features. You’ll find it on modern phones, laptops, and tablets. You can plug it in any way, which makes it very convenient.
Feature | Specification/Statistic |
Size | |
Durability | Tested up to 10,000 insertions |
Data Transfer Rate | Up to 10 Gbps for USB 3.2 |
Power Delivery | Up to 100W (20V, 5A) |
Video Support | Supports video displays up to 4K |
Audio Support | 4-channel audio including microphone support |
l Versatility: USB-C handles data, power, and video with one cable. You can charge, connect monitors, or transfer files easily.
l User Convenience: Its reversible design saves time and protects ports from damage. You don’t need to check the direction before plugging it in.
l Future-Proof: USB-C works with USB4, so it’s ready for future tech.
Fun Fact: USB-C is 60% smaller than USB-A, making it perfect for slim gadgets like ultrabooks.
USB-C has changed how we use USB connectors, offering more features and ease of use. If you upgrade, USB-C ensures your devices stay up-to-date.
Mini-USB connectors were once widely used for small gadgets. You could find them on older devices like cameras, MP3 players, and early smartphones. These connectors are smaller than USB-A and USB-B, making them great for compact electronics.
l Small Size: Mini-USB takes up less space than standard USB connectors.
l Strong Build: They are made to handle frequent plugging and unplugging.
l Dual Function: Mini-USB can transfer data and provide power, but at slower speeds compared to newer USB types.
As technology improved, Mini-USB became less common. Companies switched to Micro-USB and USB-C, which are faster and smaller. However, some older or special devices still use Mini-USB.
Tip: If your gadget has a Mini-USB port, keep a Mini-USB cable. These cables are harder to find now but are necessary for older devices.
Micro-USB replaced Mini-USB as the go-to for small gadgets. You’ve probably used it with phones, tablets, or portable chargers. It’s smaller and works better than Mini-USB, making it ideal for modern devices.
l Smaller Size: Micro-USB is tinier than Mini-USB, allowing slimmer designs.
l Better Performance: It transfers data faster and delivers more power.
l Wide Use: Micro-USB became the standard for Android phones and other gadgets.
Feature | Mini-USB | Micro-USB |
Size | Bigger | Smaller |
Data Speed | Slower | Faster |
Durability | Decent | Strong |
Micro-USB comes in two types: Micro-A and Micro-B. Micro-B is the most common and is used for charging and data transfer. Even though it’s popular, Micro-USB is slowly being replaced by USB-C, which is reversible and has more features.
Fun Fact: Micro-USB was the first standard charging port for most smartphones, reducing the need for different chargers.
Micro-USB is still used in many affordable gadgets. If you have older devices, you’ll likely need Micro-USB cables for charging and transferring data.

Standard USB ports are the ones you see most often. They are on laptops, desktops, and gaming consoles. These ports let you transfer data and provide power. You can connect devices like keyboards, mice, and flash drives to them. They work with USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and USB 3.1 versions.
These ports are great for everyday use but have limits. For example, USB 2.0 ports give only 2.5 watts of power. This is fine for small gadgets but not enough for charging bigger devices like laptops.
Tip: Need faster speeds or more power? Use USB 3.0 or newer ports.
Powered USB ports give more power than standard ones. They are perfect for charging phones, tablets, and some laptops. These ports also allow data transfer, making them very useful.
The USB Power Delivery (PD) standard decides how much power these ports can give. USB PD 1.0, for instance, provides up to 100 watts. This is enough to charge big laptops or power docking stations. Newer versions, like USB PD 3.1, can give up to 240 watts, which works for desktops and large devices.
Here’s a simple chart for USB PD 1.0:
USB Power Delivery Ver. 1.0 (2012)
Charging Profile | Voltage | Ampere (current) | Wattage (charging speed) | Devices |
1 | 5V | 2A | 10W | Phones, portable SSDs |
2 | 12V | 1.5A | 18W | Tablets, small laptops |
3 | 12V | 3A | 36W | Laptops, hubs, power banks |
4 | 20V | 3A | 60W | Big laptops, docking stations |
5 | 20V | 5A | 100W | Displays, hubs, power banks |
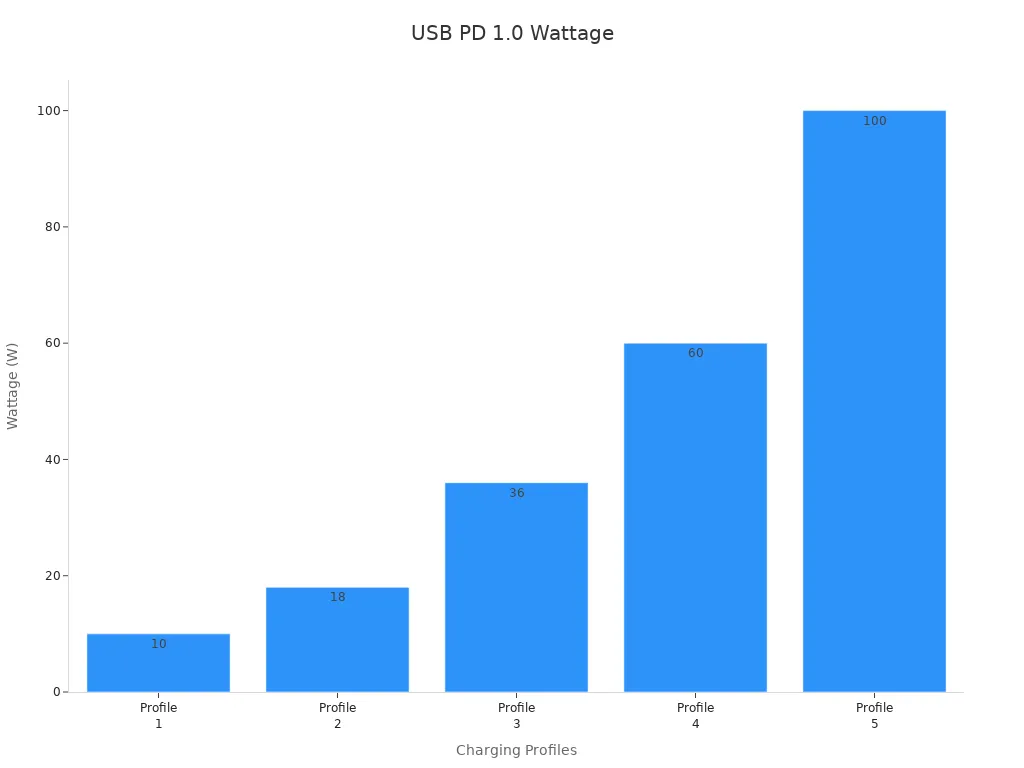
Note: High-power devices need powered USB ports. Check your device’s power needs first.
USB-C ports with Thunderbolt support are the best in USB tech. They mix USB-C’s flexibility with Thunderbolt’s speed and power. You can use them for data, charging, and video output.
Thunderbolt 4, built into USB-C, offers speeds up to 40 Gbps. It supports two 4K screens or one 8K screen, great for professionals. These ports also deliver up to 100 watts of power, enough for most laptops.
Here’s a quick look at USB-C with Thunderbolt:
Feature | Description |
Data Transfer Speeds | Works with USB 3.2 Gen 1 (5Gbps), Gen 2 (10Gbps), Gen 2x2 (20Gbps), USB4 (40Gbps) |
Power Delivery | Up to 100W under USB Power Delivery rules |
Compatibility | Supports USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and Thunderbolt 4 devices |
Design Benefits | Saves space, simplifies design, and lowers costs |
Fun Fact: Thunderbolt 4 includes PCIe support up to 32 Gbps, perfect for high-speed devices.
USB-C ports with Thunderbolt are great for modern setups. They combine many features into one port, making life easier.
USB interfaces move data using a clear system. When you plug in a device, the USB organizes data into small packets. These packets are grouped into four types: control, interrupt, bulk, and isochronous. Each type has a special job to help devices work well together. For example:
l Control packets set up and configure devices.
l Interrupt packets handle quick actions, like moving a mouse.
l Bulk packets send big files, like videos or documents.
l Isochronous packets keep audio and video streaming smooth.
To avoid mistakes, USB uses error-checking tools like Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC). If something goes wrong, it tries again to send the data. USB 3.1 made error-checking better and improved speed. Its SuperSpeedPlus encoding lowers wasted space to just 3%, making it faster than older versions.
Tip: Want faster and safer data transfer? Use USB 3.1 or newer devices.
USB interfaces also give power to devices. The USB Power Delivery (PD) system adjusts voltage based on what the device needs. For example, a USB-C charger can send 5V for phones or go up to 20V for laptops. This makes USB great for many gadgets.
Tests show how USB PD works with different connectors. Here’s a chart comparing voltage results:
Charger Name | USB Connector Type | Trigger Voltage Requested | Measured Output Voltage | Notes |
Charger A | C | 5V | 5V | Works as expected |
Charger A | C | 9V | 9V | Works as expected |
Charger A | C | 12V | 12V | Works as expected |
Charger B | A | 5V | 5V | Can’t provide 20V |
Charger F | C | 15V | N/A | No 15V output |
Charger F | C | 20V | N/A | No 20V output |
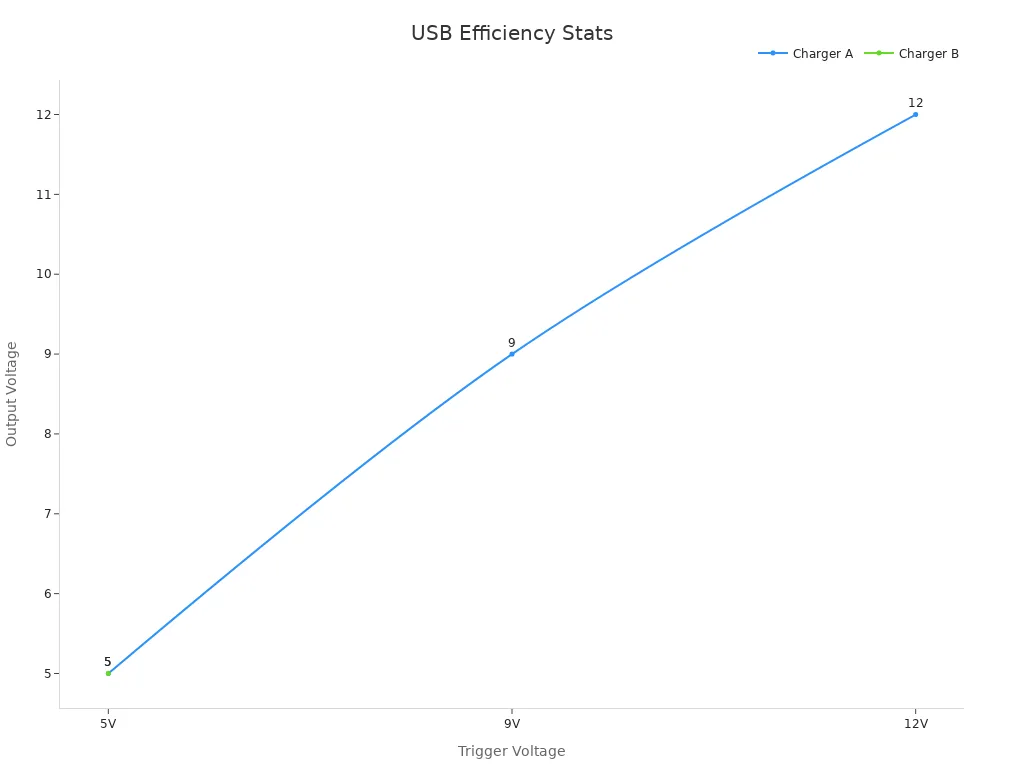
Note: USB-C chargers with PD are best for laptops and high-power devices.
Modern USB interfaces make video and audio transfer easy. USB4 can send data at speeds up to 40Gbps and works with DisplayPort for clear video. Thunderbolt 3 and 4, built into USB-C, let you use two 4K screens or one 8K screen.
Here’s a chart comparing video and audio technologies:
Technology | Data Transfer Rate | Audio/Video Support | Notes |
USB4 | Up to 20Gbps | Yes | Works with DP for video and audio. |
Thunderbolt 3/4 | Up to 20.625Gbps | Yes | Needs support for the listed speed. |
USB Power Delivery | N/A | No | Only for charging devices. |
DisplayPort | N/A | Yes | Sends high-quality video output. |
HDMI Alt Mode | N/A | Yes | Offers full HDMI 1.4b features. |
MHL Alt Mode | N/A | Yes | Mostly used for mobile devices. |
Fun Fact: USB-C audio tools, like the Zoom UAC-232, give great sound and low delay, perfect for music and podcasts.
USB interfaces make video and audio transfer simple, helping with modern multimedia setups.
USB types have changed how gadgets connect by being universal. You don’t need to worry about whether devices will work together. For example, a USB Type-A flash drive or USB Type-C cable can connect easily to many devices.
This universal design makes tech setups simpler. USB Type-C works with laptops, phones, and monitors. It reduces the need for extra cables. It also handles data transfer, charging, and video output all in one connector.
Tip: Using standardized USB connectors saves time and keeps your desk neat.
USB is made to be easy for users. You can plug in or unplug devices without restarting your computer. This is called hot-swappability. It lets you connect gadgets like keyboards or cameras while your system is on.
Studies show USB makes life easier:
l USB supports many hot-swappable devices for quick use.
l Manuals like the MC-15 guide highlight USB 2.0’s ability to transfer data and charge batteries without stopping work.
Hot-swappability is great for daily tasks. For example, you can switch devices during a presentation or game without delays.
One of USB’s best features is backward compatibility. Older devices can still work with newer USB versions. This means you don’t need to replace all your gadgets at once.
Here’s a table showing how USB connectors stay compatible:
USB Interface Type | USB 1.0 | USB 2.0 | USB3.0 | USB3.1 |
USB Type-A | √ | √ | √ | √ |
USB Type-B Standard | √ | √ |
|
|
USB Type-B 3.0 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Mini USB-A | √ | √ | √ |
|
Mini USB-B | √ | √ | √ |
|
Micro USB-A Standard | √ | √ |
|
|
Micro USB-B Standard | √ | √ |
|
|
Micro USB-A 3.0 | √ | √ | √ |
|
Micro USB-B 3.0 | √ | √ | √ |
|
USB Type-C | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Backward compatibility helps older USB gadgets work with new systems. This makes upgrading easier as technology improves.
USB types are very useful for many things. They work for jobs, fun, and everyday tasks. USB technology fits what you need.
USB helps you work better. You can connect keyboards, mice, and hard drives to your computer. USB-C hubs let you link monitors and printers with one port. This makes your desk neat and helps you work faster.
Tip: Use USB-C hubs to keep your desk tidy and connect devices easily.
USB makes entertainment better. You can plug in gaming controllers, VR headsets, or speakers. USB-C moves data quickly for smooth games and fast loading. It also sends video to 4K or 8K screens, great for movies or games.
USB isn’t just for moving data. It also charges devices well. USB Power Delivery (PD) changes power levels for your gadget. A USB-C charger can charge phones, tablets, or laptops. This makes USB great for charging.
USB works for special tasks too. Photographers use USB to move pictures from cameras to computers. Musicians use USB audio tools to record songs. Even medical devices use USB for power and data.
Fun Fact: USB-C handles both power and data, perfect for docking stations with many devices.
USB is helpful for workers, gamers, and everyone else. Its many uses make it a smart choice for almost any job.
Knowing about USB types helps you choose better gadgets and cables. You now understand how USB versions changed, the different connectors, and what each port does. This helps you pick tools for quick data transfer, easy charging, and smooth video or audio use.
USB makes connecting devices simple. It cuts down on extra wires, works with many gadgets, and supports new tech. By learning how USB works, you’re ready for future updates and can enjoy easier connections every day.
USB-A is bigger and plugs in one direction. USB-C is smaller, works both ways, and is faster. It also supports new tech like USB4 and Thunderbolt, making it better for modern gadgets.
Yes, USB 3.0 ports work with USB 2.0 devices. But the device will run at USB 2.0 speeds. To get faster speeds, use a USB 3.0 device and cable.
USB-C is fast, powerful, and can send video. It works with USB4 and Thunderbolt, so it’s ready for new tech. Its reversible design and many uses make it great for today and tomorrow.
Check your device’s manual or specs. Devices with USB-C often support PD. Look for “PD” or watt numbers (like 100W) on chargers or cables to be sure.
No, USB-C cables vary in speed, power, and video features. Some only charge, while others transfer data or video. Always check the cable’s details to match your needs.